Kepler's Laws
Kepler's Laws: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion, Kepler's Law of Orbits, Kepler's Law of Areas, Kepler's Law of Periods, Explanation of Kepler's Laws, Geocentric Theory of Solar System & Areal Velocity of Planets etc.
Important Questions on Kepler's Laws
Assertion: Areal speed of planets moving around the sun remains constant.
Reason: Gravitational force between planet and sun provides required centripetal force to the planet for revolution around the sun.
The _____ vector drawn from the sun to the planet sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time.
As the distance of the planet from the sun increases, the period of revolution decreases
Figure shows elliptical orbit of a planet about the sun .The shaded are is twice the shaded area . If is the time for the planet to move from and and is the time to move from and , then .
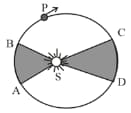
Kepler's second Law states that the line connecting the planet and the Sun covers unequal areas in equal intervals of time.
A planet moving around the sun sweeps area in days, in days and in days, then find the relation between , and .
According to Kepler's second law of planetary motion, the areal velocity of a planet revolving around the sun
What do you understand by the areal velocity of a planet?
Assume that the earth moves around the sun in a circular orbit of radius and there exists a planet which also move around the sun in a circular orbit with an angular speed twice as large as that of the earth. The radius of the orbit of the planet is
A body is projected from earth's surface to become its satellite, its time period of revolution will not depend upon
The annual variations of solar power incident per unit area at a particular point on the Earth's surface is mainly due to the change in the
Observe the given figure showing the orbit of a planet moving around the Sun and fill in the blank given below:
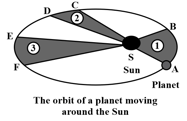
Kepler's third law states that the square of the period of revolution of a planet around the Sun is directly proportional to the cube of its mean _____ from the Sun.
Observe the given figure showing the orbit of a planet moving around the Sun and fill in the blank given below:
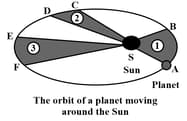
Kepler's second law states that the line joining the planet and the Sun sweeps equal areas in equal intervals of _____.
Observe the given figure showing the orbit of a planet moving around the Sun and fill in the blank given below:
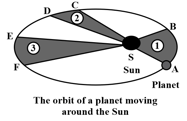
Kepler's first law states that the orbit of a planet is a/an _____ with the Sun at one of the foci.
